AgriTech Revolution: Transforming African Agriculture Through Digital Literacy
Agriculture is the backbone of Africa's economy, contributing over 32% of GDP and employing nearly 65% of the workforce1. In Cameroon, agriculture accounts for about 20% of GDP and employs over 70% of the rural population. Despite its potential, the sector faces challenges, including low productivity, poor infrastructure, limited market access, and the increasing effects of climate change.
AgriTech, powered by digital literacy, offers transformative solutions. From mobile platforms that provide real-time market prices to drone technology monitoring crop health, digital tools are revolutionizing farming practices. However, realizing these benefits requires a strategic and inclusive approach tailored to Cameroon’s unique agricultural landscape.
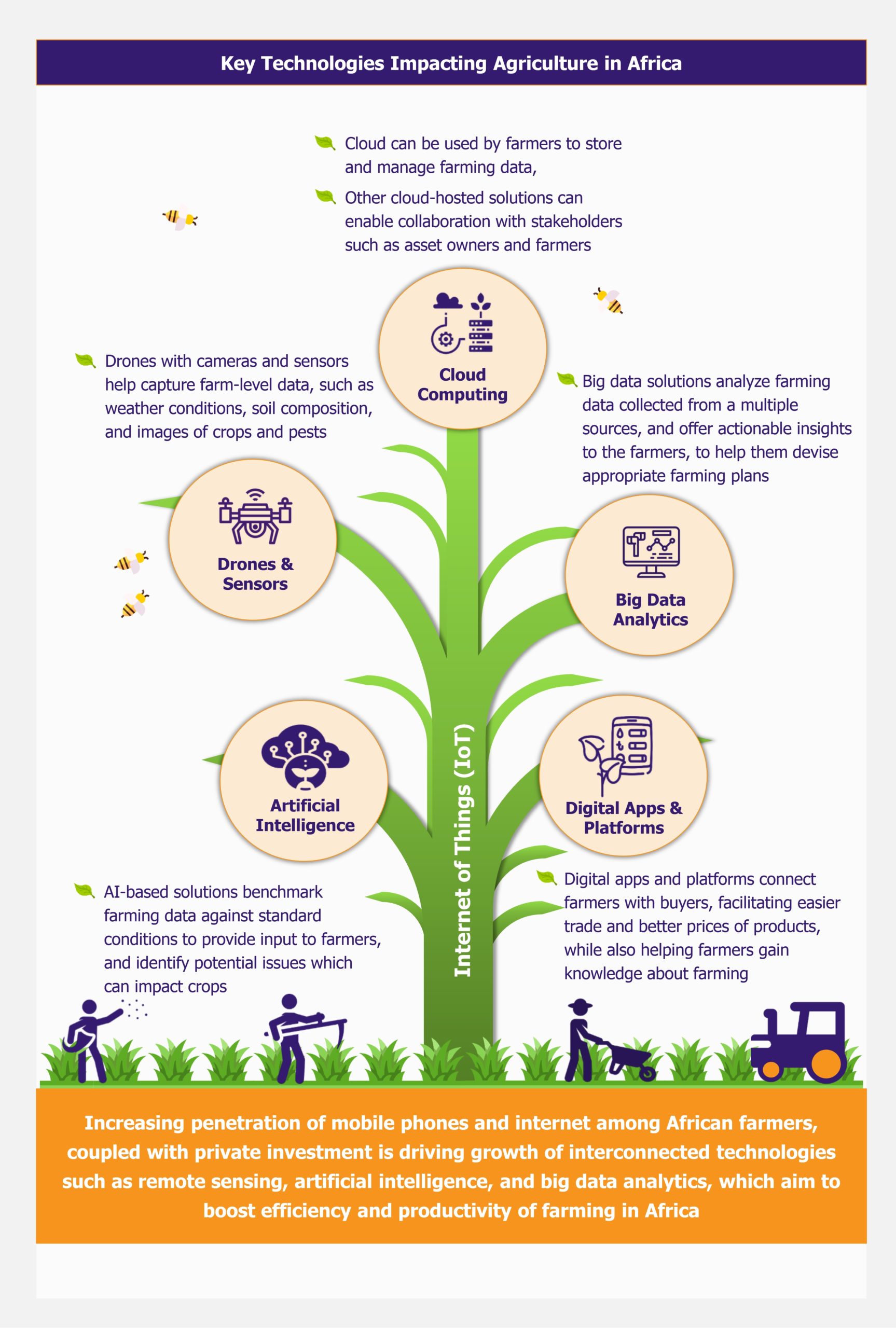
The Impact of AgriTech on African Farming
AgriTech encompasses innovations like precision farming, smart irrigation systems, and digital platforms that connect farmers to markets. These technologies help smallholder farmers, who constitute 80% of Africa’s agricultural workforce, enhance productivity while reducing costs and environmental impact 2.
Key Benefits:
• Enhanced Productivity: Precision agriculture tools enable farmers to monitor crop health, optimize input usage, and increase yields. Digital tools such as drones, satellite imaging, and IoT-enabled devices help farmers monitor soil health, crop status, and water usage.
• Market Access: Digital platforms connect farmers directly with buyers, reducing reliance on intermediaries and improving profit margins.
• Financial Inclusion: Mobile banking and digital payment systems facilitate access to credit and financial services, empowering farmers to invest in their operations.
• Climate Resilience: AgriTech solutions provide real-time weather data and climate-smart farming practices, helping farmers adapt to changing environmental conditions. Tools like weather forecasting apps and AI-powered analytics help farmers make data-driven decisions, reducing vulnerability to climate variability.
• Education and Skill Building: Online platforms offer farmers training in modern techniques, pest management, and sustainable farming practices.
Case Studies of Successful AgriTech Ventures in Africa
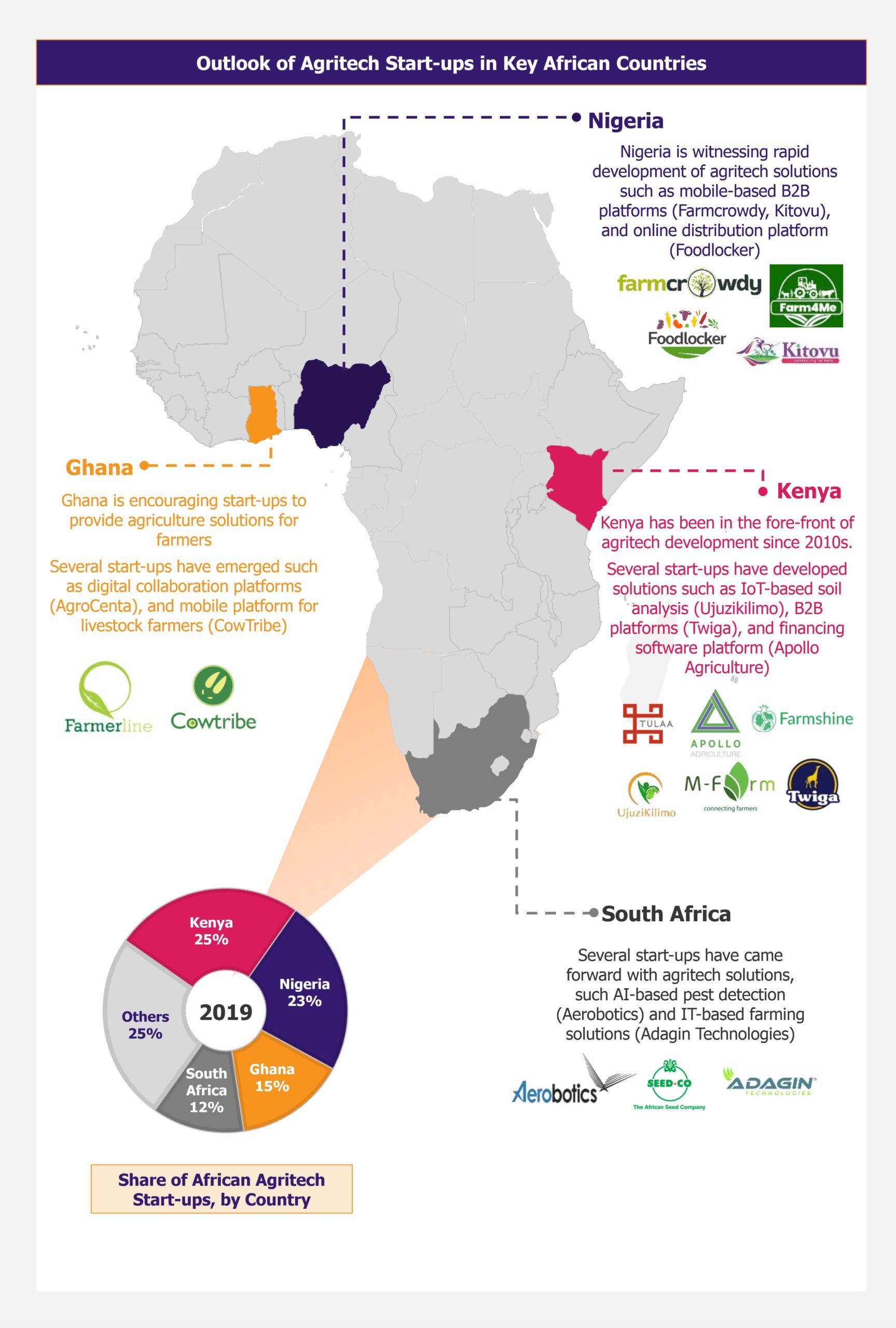
1. Agrix Tech (Cameroon) 3: This startup utilizes artificial intelligence to help farmers diagnose crop diseases and recommend treatment options, enhancing crop health and productivity.
2. Freshbag (Cameroon) 4: Serving as a bridge between producers and small retailers, Freshbag leverages digital solutions to streamline the supply chain, ensuring fresh produce reaches urban markets efficiently.
3. ThriveAgric (Nigeria) 5: Featured in London Business School’s case study series, ThriveAgric provides farmers with access to finance, premium markets, and data-driven advisory services, significantly boosting productivity and income.
4. Digital Green (Regional) 6: Provides video-based agricultural education tailored to rural communities.
An Action Plan for AgriTech Implementation in Africa
To fully unlock the potential of AgriTech, Africa needs a multi-dimensional action plan focusing on infrastructure, training, and governance.
1. Enhance Digital Literacy
• Training Programs: Roll out nationwide digital literacy campaigns targeting rural farmers, especially women and youth.
• Curriculum Integration: Integrate AgriTech training modules into agricultural colleges and technical schools.
• Community-Based Training Hubs: Establish digital resource centres in farming communities.
2. Improve Infrastructure
• Internet Connectivity: Expand broadband infrastructure in rural regions to ensure reliable internet access.
• Sustainable Energy: Promote the use of solar power solutions to enable uninterrupted digital operations on farms.
3. Develop Farm-to-Market Roads
• Government Investment: Prioritize the construction and maintenance of farm-to-market roads to ensure efficient transportation of produce.
• Local Partnerships: Engage local governments and municipalities in identifying and maintaining essential road networks.
• Impact: Reduce post-harvest losses, lower transportation costs, and improve market accessibility for rural farmers.
4. Create and Support Farmer Cooperative Unions
• Formation of Unions: Encourage farmers to form cooperative unions to pool resources, share knowledge, and negotiate better prices.
• Capacity Building: Provide financial management training and workshops on cooperative governance.
• Access to Finance: Enable cooperatives to secure larger loans and investments through collective bargaining.
• Digital Platforms: Create online cooperative management systems for transparent financial tracking and communication.
5. Strengthen Public-Private Partnerships
• AgriTech Startups: Provide financial incentives for startups developing agricultural solutions tailored to local needs.
• Private Sector Investment: Encourage private companies to invest in rural farming technologies.
• Research Collaboration: Partner with universities and agricultural research institutes to drive innovation.
6. Facilitate Access to Finance
• Digital Banking Services: Expand access to mobile banking services for seamless transactions and savings.
• Microloans and Grants: Create loan programs specifically for farmers adopting AgriTech solutions.
• Insurance Schemes: Introduce crop insurance schemes to reduce risks associated with unpredictable farming seasons.
7. Promote Cultural Shifts and Awareness
• Community Engagement: Launch campaigns highlighting the economic benefits of digital farming.
• Success Stories: Showcase local farmer success stories to inspire others to adopt AgriTech tools.
• Role Models: Empower female farmers as ambassadors for AgriTech adoption.
8. Policy and Regulatory Frameworks
• Clear Policy Guidelines: Develop a National AgriTech Policy focusing on inclusivity, transparency, and sustainability.
• Data Privacy Regulations: Ensure strict data protection laws to safeguard farmers' data.
• Monitoring and Evaluation: Implement periodic reviews of AgriTech initiatives to track progress.
The Way Forward: A Unified Effort
For Africa to fully embrace the AgriTech revolution, stakeholders must work in unison:
• Government: Provide policies, infrastructure, and funding.
• Private Sector: Invest in tech-driven farming solutions and rural outreach programs.
• NGOs: Focus on awareness campaigns, training, and advocacy.
• Farmers: Actively participate in cooperative unions and embrace modern digital tools.
The integration of AgriTech into Cameroon's agricultural sector holds immense potential to enhance productivity, improve livelihoods, and drive economic growth. By focusing on digital literacy and creating an enabling environment for technological adoption, Cameroon can lead the way in transforming African agriculture for a sustainable future.
What are your thoughts on the AgriTech revolution in Africa? Share your insights and experiences!



